-
Super-Resolution Ultrasound Localisation Microscopy (SRUS/ULM)
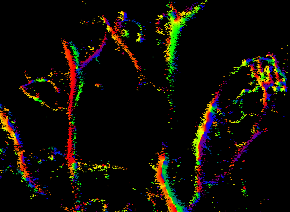
Introduction The spatial resolution of any imaging modality based on waves (electro-magnetic or mechanical) is fundamentally limited by the size of its wavelength (diffraction-limited image resolution). In biomedical ultrasound imaging this diffraction limit has resulted in an inherent compromise between spatial resolution and penetration depth. Recently such diffraction limit has been broken in the field of…
-
Vascular Flow Imaging
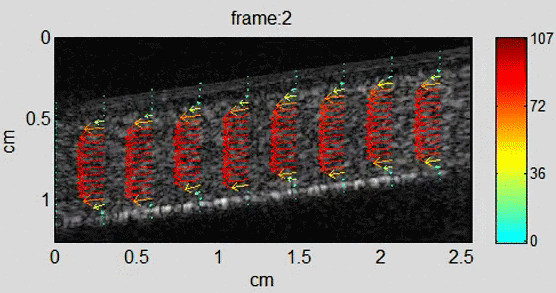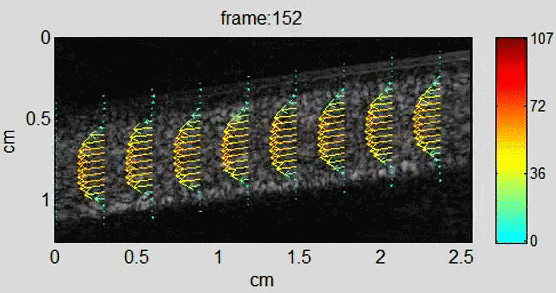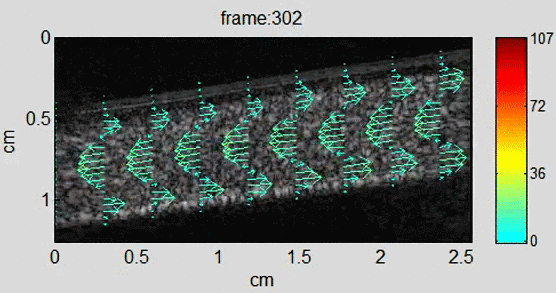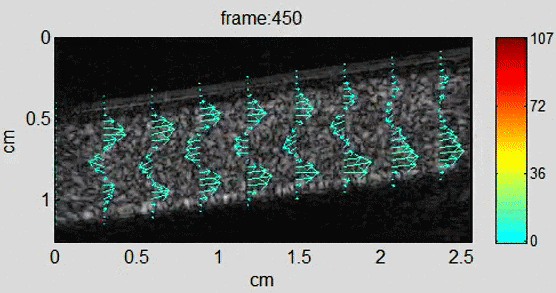
Background In recent years, echo particle image velocimetry (ePIV), also known as ultrasound particle image Velocimetry (uPIV), has shown to be able to map flow velocity distribution in vivo. The technique provides valuable information about blood flow and flow induced stress on vessel wall for studying cardiovascular diseases. Using sequential ultrasound B-mode (or contrast specific)…
-
Cardiac Imaging and Image Analysis
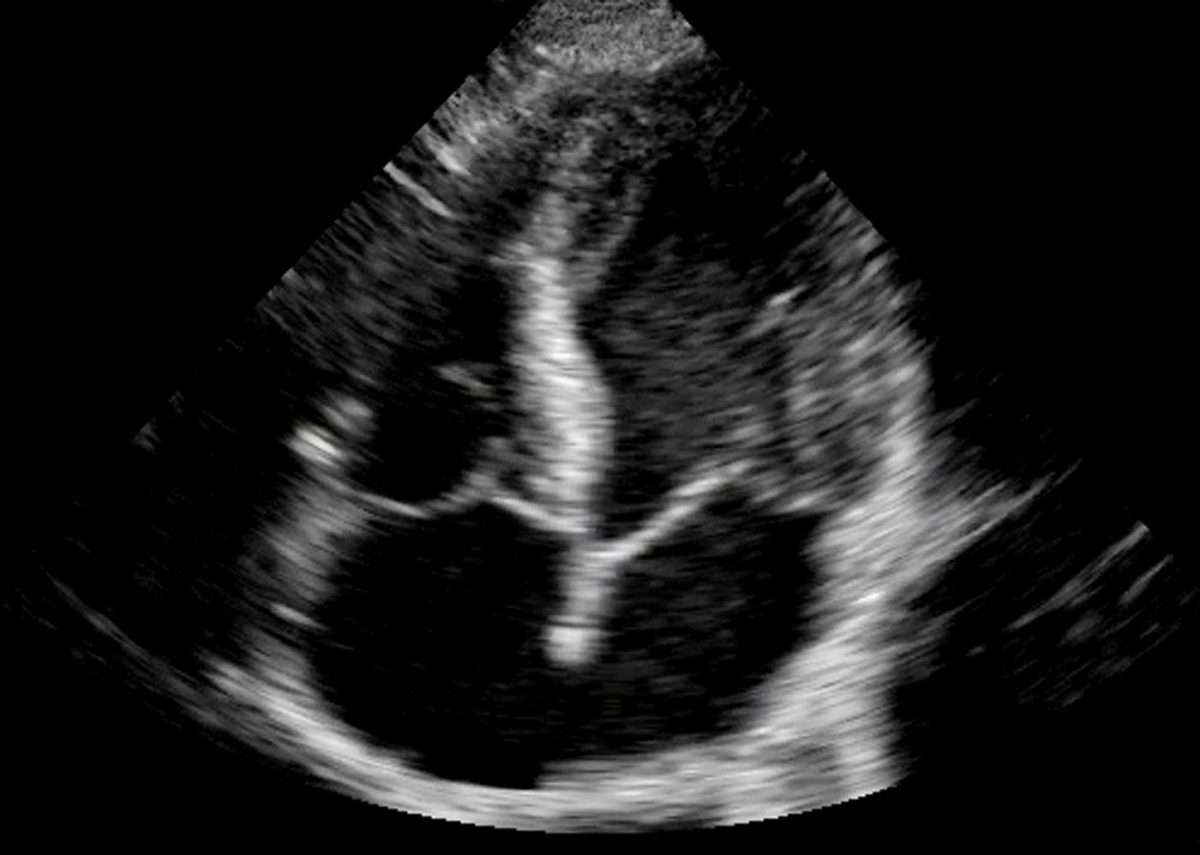
Ultrasound and microbubble contrast agents offer imaging and quantifying microcirculation / perfusion within the myocardium. Perfusion defects are an early indicator of coronary heart diseases as opposed to the current clinical practice which still relies on detection of cardiac wall motion abnormalities. We are interested in developing novel imaging (e.g. high frame rate imaging) and…
-
Ultrafast Contrast Image Acquisition

The recent advancement in digital parallel processing technology has paved the path for very high frame-rate ultrasound imaging based on holographic concepts. Such methods remove the need of line by line scanning, allowing for the reconstruction of an entire ultrasound image from a single transmission. One of the major implications of such methods is the…
-
Bubble Physics
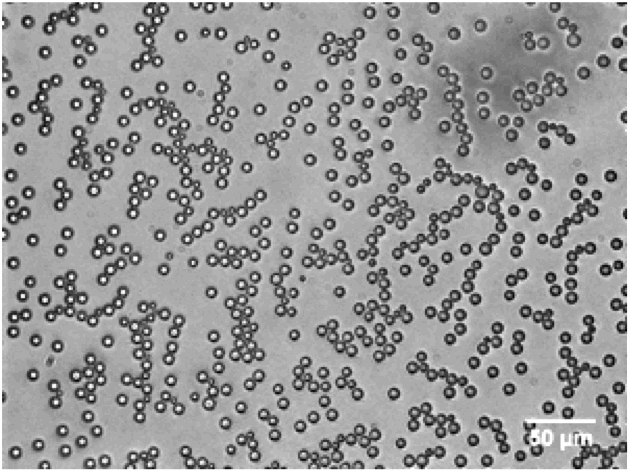
Microbubbles have shown great promise as ultrasound contrast agents and have been used in a range of clinical applications including cardiovascular diseases and cancer. They are extremely sensitive as contrast agents – under the right ultrasound frequency a single micron-sized bubble can be detected, as they can resonant under ultrasound and oscillate in a highly…
-
Cancer and Molecular Imaging
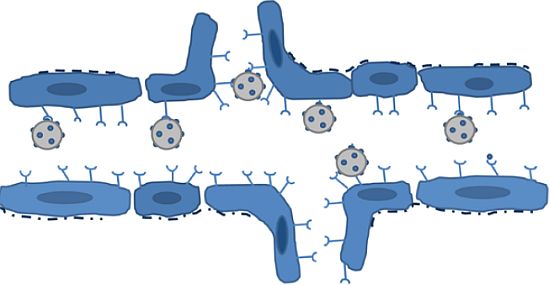
The development of microbubble contrast agents for ultrasound (US) imaging has made visualisation and quantification of blood flow in micro-vasculature possible. Such imaging technique can be applied to the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of clinical conditions such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Recently adapting the microbubbles to target specific molecules within the…
-
Brain Imaging
Ultrasound imaging of the brain is very challenging for traditional reconstruction algorithms. This is for two reasons. First, the strong reflected signal from the skull swamps the weak reflected signal from the brain. Second, algorithms for traditional ultrasound reconstruction cannot account for multiple-scattering in the skull. Instead full-waveform inversion (FWI) has been proposed to reconstruct…